Knowing how to measure thread size is essential when working with bolts, screws, nuts, and threaded holes. Accurate thread measurement ensures that fasteners fit properly, create secure connections, and perform reliably over time. Incorrect measurements can lead to stripped threads, loose joints, or parts that simply do not fit.
Whether you are replacing a fastener, assembling machinery, or ordering custom components, understanding how to measure threads helps prevent errors and saves time. Even small differences in diameter or thread pitch can affect compatibility and the overall strength of the assembly.
This guide explains how to measure threads, how to measure bolt size, and how to determine thread size using practical methods and clear, easy-to-follow steps. It is designed for beginners as well as professionals who want accurate, reliable results and long-lasting, safe performance of all threaded components.

What Is Thread Size and Why It Is Important
Thread size refers to the standard dimensions of the spiral ridges found on bolts, screws, and threaded holes. These dimensions control how securely a fastener connects with its matching part. When the thread size is correct, the connection fits smoothly, holds firmly, and stays secure during use.
Proper measuring thread size is important because even small differences in diameter or pitch can cause problems. Incorrect thread measurement often leads to cross threading, loose fittings, or damaged threads, especially in mechanical and structural applications.
Understanding thread size is not just about choosing the right fastener. It also helps improve safety, strength, and long term durability. Knowing how to measure thread size correctly prevents failures, reduces wear, and ensures reliable performance in all types of projects.
Basic Elements of a Thread
Before learning how to measure thread size, it is important to understand the basic parts of a thread. Threads are the spiral ridges and grooves that wrap around bolts, screws, and inside threaded holes. These ridges help fasteners grip and hold parts together securely.
The major diameter is the widest measurement taken across the outer ridges of the thread. The minor diameter is the smallest measurement found between the grooves. Both measurements play an important role in identifying the correct thread size.
Thread pitch or threads per inch describe how closely the threads are spaced along the fastener. This spacing affects how smoothly parts fit together. When these measurements are understood, accurate thread measurement becomes much easier and more reliable.
Metric vs Imperial Thread Systems
One of the most common challenges when learning how to determine thread size is identifying whether a thread is metric or imperial. These two systems use different measurement standards and are not designed to work together, even if the threads look similar at first glance.
Metric threads are measured in millimeters and defined by their diameter and thread pitch. Imperial threads are measured in inches and identified by diameter and threads per inch. This difference in measurement method is a key factor in proper thread identification.
Because metric and imperial threads can appear almost identical, small differences in pitch often cause fitting problems. Accurate thread measurement helps eliminate this confusion and ensures fasteners engage smoothly and securely.
Tools Required for Measuring Thread Size
Using the right tools makes measuring thread size faster and more accurate. While advanced tools are used in professional environments, the following are sufficient for most applications:
-
- Digital or vernier calipers for measuring thread diameter
-
- Thread pitch gauge for identifying pitch or TPI
-
- Steel ruler for basic measurements
-
- Nut and bolt gauge for quick identification
Having these tools on hand improves consistency when learning how to measure threads.
How to Measure Thread Size Step by Step
This section explains the practical process of how to measure thread size in a clear, repeatable way.
- Identify the Thread Type
Determine whether the thread is external, like on a bolt or screw, or internal, such as in a nut or tapped hole. For internal threads, you can refer to type of thread taps to ensure correct sizing. - Measure the major diameter
Use calipers to measure across the widest part of the thread. This step is critical for how to measure bolt size. - Measure thread pitch or TPI
Use a thread pitch gauge or count threads over a measured distance. - Confirm with a thread chart
Match your measurements to a standard chart to verify the exact size.
Following these steps ensures reliable thread measurement results.
How to Measure Bolt Size Correctly
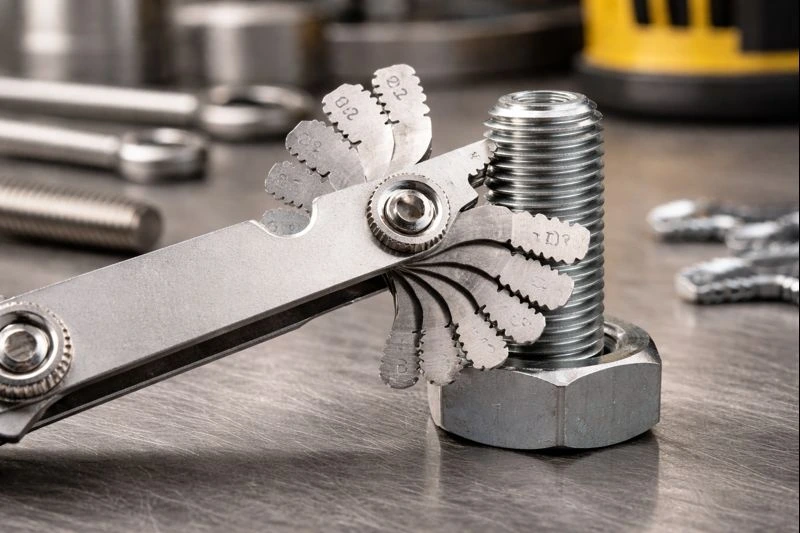

Understanding how to measure bolt size involves more than checking the thread diameter. Bolt size is defined by three key factors: diameter, length, and thread pitch. Each of these measurements plays an important role in how the bolt fits and functions.
The diameter determines how thick the bolt is, while the length controls how deep it can be installed into a component. Measuring both correctly helps ensure the bolt provides proper strength and support in its application.
Thread size is a crucial part of bolt size, especially when choosing replacement fasteners. Without accurate thread measurement, even a bolt with the correct diameter and length may not fit properly or hold securely.
Measuring External Threads on Bolts and Screws
External threads are easier to measure because they are fully exposed. When measuring external threads, focus on consistency and alignment.
-
- Measure the outer diameter across thread crests
-
- Identify pitch using a thread gauge
-
- Double-check measurements to avoid errors
This method is widely used for measuring thread size in manufacturing and repair work.
Measuring Internal Threads in Nuts and Tapped Holes
Internal thread measurement requires extra care because the threads are inside a nut or tapped hole and harder to access. When learning how to measure thread size internally, measuring the inside diameter accurately is critical, as even small errors can lead to incorrect sizing and poor fit.
Using calipers designed for internal measurements helps improve accuracy when measuring thread size. A thread pitch gauge is also useful for identifying thread spacing, making it easier to understand how to measure threads correctly in tight spaces.
When possible, test-fitting a known bolt is an effective way to confirm results. This method helps verify how to determine thread size and ensures the internal threads match properly before installation or replacement.
How to Figure Out Thread Size Without Special Tools
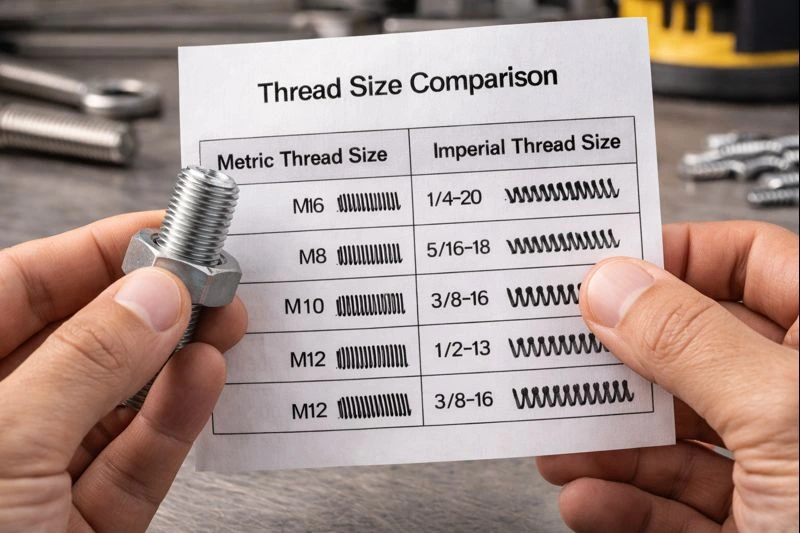
If specialized tools are not available, you can still learn how to figure out thread size using simple methods. Counting threads over a measured distance gives a good estimate of the thread pitch, allowing you to start measuring thread size without professional tools.
You can also compare the threads to known bolts, screws, or nuts. Matching the diameter and pitch visually or by trial fit helps identify the approximate size and is useful when learning how to measure threads quickly.
While these methods are helpful for quick checks, they are not as precise as using proper instruments. For accurate and reliable thread measurement, tools like digital calipers or thread pitch gauges are recommended to ensure a proper fit and prevent thread damage.
Using Thread Size Charts Effectively
Thread charts simplify how to determine thread size once basic measurements are taken.
-
- Match diameter and pitch values
-
- Identify standard metric or imperial sizes
-
- Reduce guesswork and errors
Thread charts are especially useful when measuring thread size frequently.
Common Thread Measurement Mistakes
Mistakes during thread measurement are common but avoidable. Be cautious of the following:
-
- Mixing metric and imperial systems
-
- Measuring worn or damaged threads
-
- Miscounting threads per inch
-
- Measuring at an angle
Avoiding these issues improves accuracy and reliability.
Practical Applications of Thread Measurement
Accurate thread measurement is essential in automotive systems, industrial machinery, plumbing fittings, and custom metal fabrication. In all these applications, using the correct thread size ensures strong connections, reliable performance, and safe operation. Proper sizing also prevents mismatched fasteners and avoids costly errors during assembly or repair.
Knowing how to measure thread size correctly helps reduce downtime, prevent damage to components, and improve overall efficiency. It ensures that bolts, screws, and nuts fit properly, maintain structural integrity, and last longer. Accurate thread measurement is a small step that makes a big difference in the durability and safety of any project.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I measure thread size at home?
Yes, basic tools can be used for simple thread measurement, though accuracy may vary.
What is the most accurate method?
Digital calipers combined with a thread pitch gauge provide the most reliable results for measuring thread size.
How do I identify metric vs imperial threads?
Measuring pitch or TPI and comparing with a chart helps determine thread size accurately.
Conclusion
Learning how to measure thread size is a valuable skill for anyone working with fasteners or threaded components. By combining proper tools, clear steps, and careful verification, you can achieve accurate thread measurement every time.
Whether you are learning how to measure bolt size, identifying internal threads, or trying to figure out thread size for a replacement part, taking the time to measure correctly saves effort, reduces errors, and ensures reliable results.






